Counties in Oklahoma where landslides pose the greatest threat
In Oklahoma, over half of the land is susceptible to landslides in 6 counties.
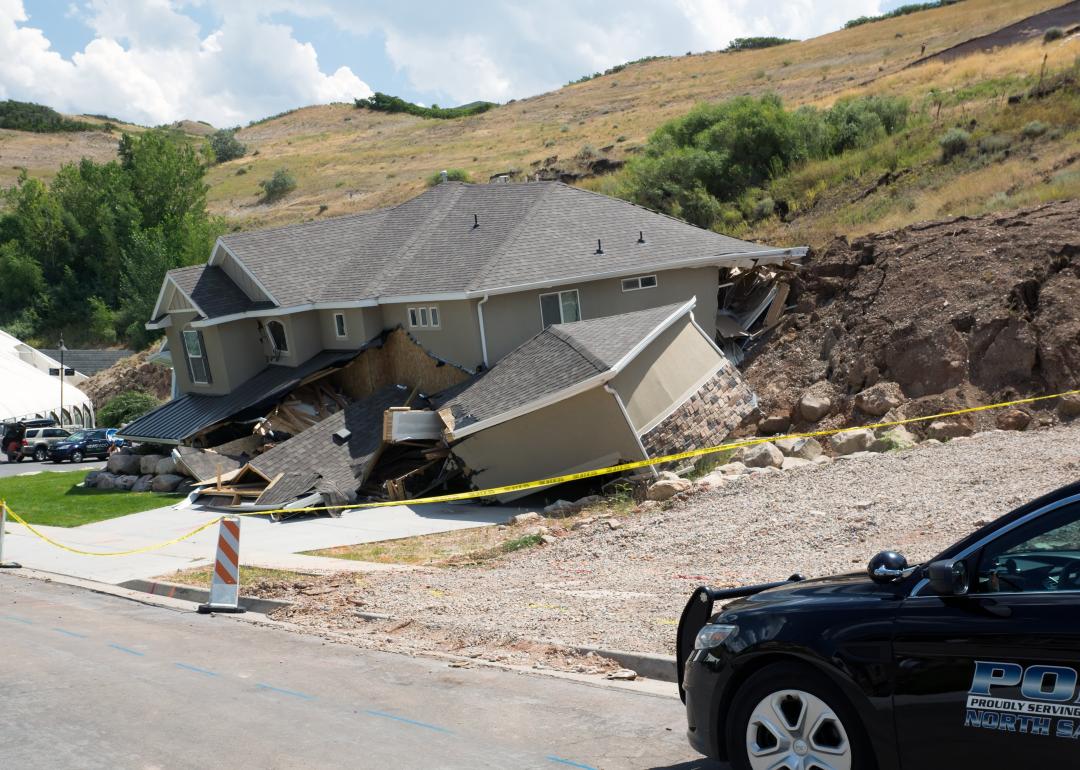
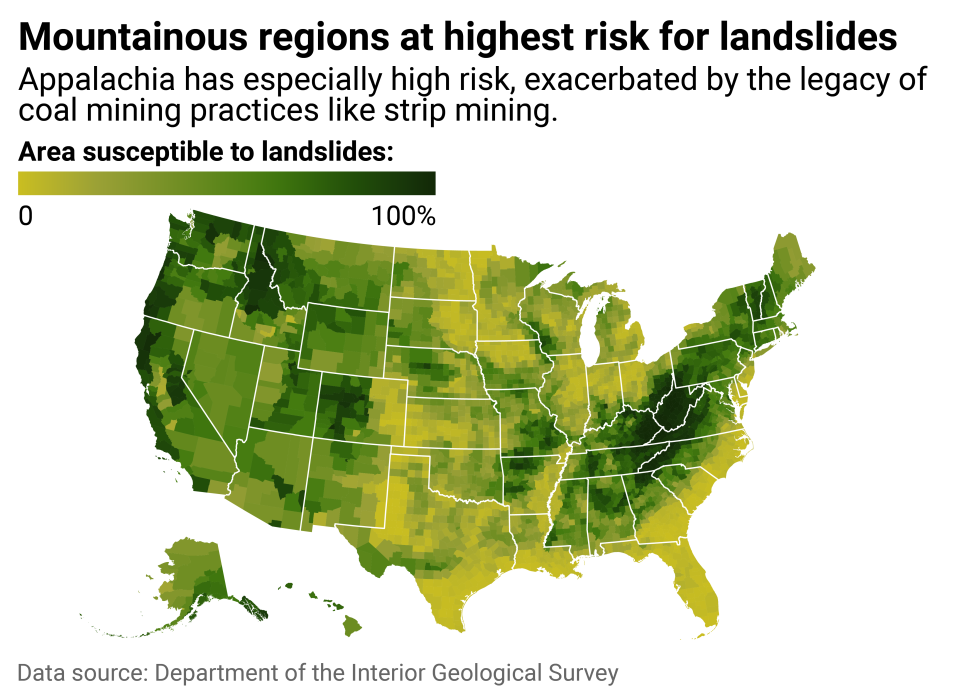
A landslide occurs when rock, debris, or earth moves down a slope. Inclines like hills and bluffs are a critical element of slides, meaning mountainous regions are at higher risk. Typically, landslides are triggered by forces like heavy rainfall, snowmelt, earthquakes, volcanic activity, human activities, or some combination of factors. Often, they're impossible to predict.
According to the Geological Survey, places where weak or fractured earth sit on steep slopes are likely to experience landslides—for example, areas with a history of strip mining. In Appalachia, about 1,400 square miles of land are scarred by strip mining within the Ohio River basin, according to an Inside Climate News analysis of satellite imagery. Together, the "waste rock" left behind, increasing stream flows, and heavy rainfalls brought on by climate change create a deadly recipe for landslides. This part of Appalachia is also near the Gulf of Mexico, where fast-warming waters stir up exceptionally fast-growing storms, as was the case with Hurricane Helene.
Combined, these elements create the highest vulnerability to landslides in the region. Much of West Virginia, in particular, is at risk: In 47 of the state's 55 counties, more than 90% of the land is susceptible to slides. Parts of Virginia, Kentucky, Ohio, Tennessee, and North Carolina are also exceedingly vulnerable.
Parts of California's coastline have also been plagued by major landslides. Earlier this year, a rockslide destroyed a part of Highway 1 along the state's famed Big Sur. The earth below the highway isn't sturdy, and wetter storms are further weakening it, contributing to more frequent and severe landslides. The majestic Big Sur stretch is an iconic road trip and tourism destination, where the highway winds along cliffs above the Pacific Ocean. However, it was forced to close to most traffic, and still offers just one lane at some points.
Other landslide risk factors include population growth, rapid land use changes, urbanization, heavy logging and deforestation, and inappropriate use of lands—slopes in particular. Wildfires also generate landslide hazards, leaving behind excess debris that can be dragged down during floods, as was the case in Big Sur.
The heightened frequency and severity of landslides are a direct consequence of logging, mining, and climate change, with massive repercussions for safety and critical infrastructure in the U.S. and around the world.
Hazard maps like those from the Geological Survey are a tool that federal, state, and local governments can use to identify landslide vulnerabilities and prepare for them. Preparation and mitigation efforts might include landslide drills, evacuation plans, improved drainage systems, and slope stabilization. Governments in susceptible areas can adopt disaster-resilient building codes and standards, as well as restrictions on mining and logging.
In some cases, such as Highway 1, there are no obvious solutions to fully protect against landslides. Still, with increased awareness and response plans, people can make more informed decisions on where to live (or safely visit) and can prepare themselves for landslides and their aftermath.
Read on to see where in Oklahoma is most vulnerable to the growing landslide threat.
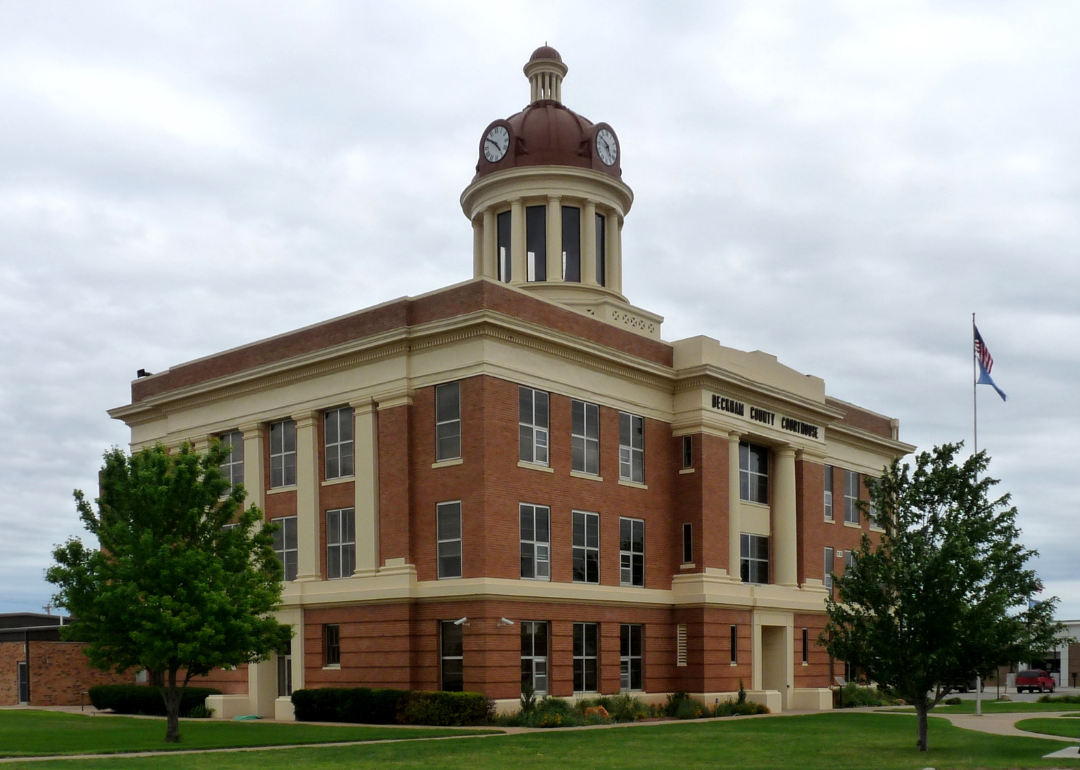

- Percent susceptible area: 22.6%
- Total susceptible area: 204 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 22.8%
- Total susceptible area: 147 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 23.2%
- Total susceptible area: 110 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 24.5%
- Total susceptible area: 227 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 24.6%
- Total susceptible area: 144 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 24.6%
- Total susceptible area: 200 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 25.0%
- Total susceptible area: 195 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 25.5%
- Total susceptible area: 174 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 26.1%
- Total susceptible area: 143 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 26.1%
- Total susceptible area: 280 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 26.3%
- Total susceptible area: 290 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 26.6%
- Total susceptible area: 327 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 26.9%
- Total susceptible area: 178 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 27.3%
- Total susceptible area: 172 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 27.5%
- Total susceptible area: 160 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 28.8%
- Total susceptible area: 238 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 29.1%
- Total susceptible area: 152 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 29.8%
- Total susceptible area: 382 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 30.1%
- Total susceptible area: 157 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 30.4%
- Total susceptible area: 191 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 30.6%
- Total susceptible area: 380 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 31.5%
- Total susceptible area: 328 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 31.6%
- Total susceptible area: 313 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 32.0%
- Total susceptible area: 239 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 32.1%
- Total susceptible area: 233 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 33.2%
- Total susceptible area: 194 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 33.4%
- Total susceptible area: 263 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 33.8%
- Total susceptible area: 126 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 33.8%
- Total susceptible area: 325 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 34.3%
- Total susceptible area: 328 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 34.9%
- Total susceptible area: 241 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 35.9%
- Total susceptible area: 151 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 36.3%
- Total susceptible area: 208 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 38.0%
- Total susceptible area: 310 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 38.7%
- Total susceptible area: 509 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 38.9%
- Total susceptible area: 382 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 39.9%
- Total susceptible area: 515 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 40.0%
- Total susceptible area: 255 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 40.6%
- Total susceptible area: 275 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 41.3%
- Total susceptible area: 474 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 41.5%
- Total susceptible area: 940 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 45.1%
- Total susceptible area: 433 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 45.6%
- Total susceptible area: 459 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 47.4%
- Total susceptible area: 888 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 55.0%
- Total susceptible area: 773 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 55.3%
- Total susceptible area: 417 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 55.7%
- Total susceptible area: 889 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 56.9%
- Total susceptible area: 424 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 57.9%
- Total susceptible area: 421 square miles

- Percent susceptible area: 66.6%
- Total susceptible area: 384 square miles
This story features data reporting and writing by Paxtyn Merten and is part of a series utilizing data automation across 50 states.
